Fraudsters are increasingly posing as online bookmakers to encourage victims to click on links that will infect their computers with malware or lead them to sites where their banking info will be stolen.
A new report by cybersecurity solutions provider Group-IB details the types of threats it has seen in malicious emails during the first half of 2020. The company says it blocked 9,304 phishing web resources in H1 2020, up 9% over the first half of 2019.
Disturbingly, Group-IB says 69% of these resources used safe SSL/TLS connection, up from 33% at the end of 2019. Sites lacking SSL/TLS certificates are often flagged by web browsers before a victim is allowed to proceed, thereby diminishing the effectiveness of phishing efforts, but fake or forged certificates are increasingly available on the dark web.
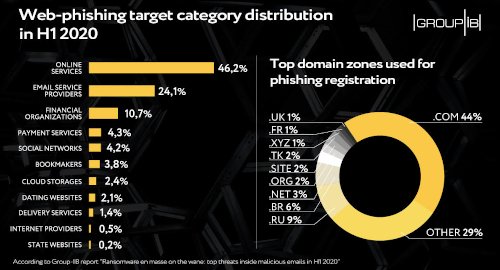
Emails purporting to come from legit online services accounted for 46.2% of malicious emails, while email service providers ranked second with 24.1%. Financial organizations (10.7%), payment services (4.3%) and social networks (4.2%) filled out the top-five.